Naval Aircraft
Fskl
Facilty for traffic,communications and logistic
Seminar Paper
Naval Aircraft
Professor: Student:
Dr Jelena Lekić
Berane,April 2013
Content :
1
1.Introduction-------------------------------------------------- --3
2.Structural stress---------------------------------------- -------3
2.1Tension--------------------------------------------------------3
2.2 Conpresion------------------------------------------ ---------3
2.3 Shear---------------------------------------------------------4
2.4 Bending-------------------------------------------------------4
2.5 Tersion-------------------------------------------------------4
3.Construction materials-----------------------------------------5
4. Fixed wing aircraft---------------------------------------------5
4.1 Fuselage------------------------------------------------------5
4.2 Wings---------------------------------------------------------6
4.3 Stabilizers----------------------------------------------------7
5.Flight control surfaces-----------------------------------------8
5.1 Primary group------------------------------------------------8
5.2 Secondary group---------------------------------------------8
5.2.1 Wing flaps--------------------------------------------------9
5.2.2 Spoilers ----------------------------------------------------9
5.2.3 Speed brakes ----------------------------------------------9
5.2.4 Slats-------------------------------------------------------10
5.2.5 Light control mechanism---------------------------------10
6. Landing gear-------------------------------------------------10
6.1 Arresting gear-----------------------------------------------11
6.2 Catapult equipment-----------------------------------------12
7.Summary------------------------------------------------------13
8.Bibliography---------------------------------------------------14
2
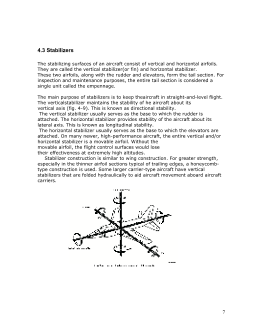
2.3 SHEAR
Cutting a piece of paper with scissors is an exampleof a shearing action. In an
aircraft structure, shear (fig.4-1, view D) is a stress exerted when two pieces of
fastened material tend to separate. Shear stress is then outcome of sliding one
part over the other in opposite directions. The rivets and bolts of an aircraft
experience both shear and tension stresses
2.4 BENDING
Bending (fig. 4-1, view E) is a combination of tension and compression. For
example, when bending a piece of tubing, the upper portion stretches (tension)
and the lower portion crushes together (compression). The wing spars of an
aircraft in flight are subject to bending stresses.
2.5TORSION-
Torsional (fig. 4-1, view C) stresses result from a twisting force. When you wring
out a chamois skin, you are putting it under torsion. Torsion is produced in an
engine crankshaft while the engine is running. Forces that produce torsional
stress also produce torque.
4
Ovaj materijal je namenjen za učenje i pripremu, ne za predaju.
Slični dokumenti