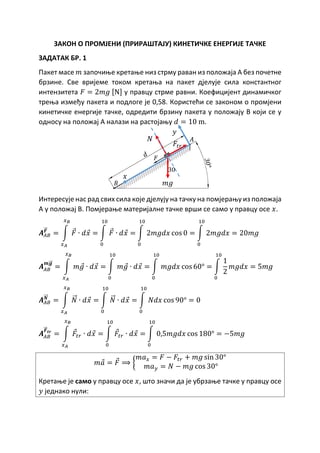
Business environment scanning Pregled
1132
BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT SCANNING:
PREREQUISITE FOR SUSTAINABLE LEARNING COMPANY
Nataša RUPČIĆ ,
Ekonomski fakultet u Rijeci, Ivana Filipovića 4, 51001
Rijeka
Senka BOROVAC ZEKAN
Sveučilišni studijski centar za stručne studije u Splitu, Livanjska 5, 21000 Split
Abstract:
The overall corporate performance is dependent upon various constituents, both internal, as
well as external. The long term sustained competitive advantage can therefore be based on
continual scanning and reflection upon environmental constituents. Despite the fact that most
of these changes come from initiatives within, it is essentially the impulses from the external
environment that drive the redesign of organizational mental models following modifications
of other organizational constituents. In that sense, the learning company represents a suitable
platform on which basis the modern business can be developed, since it offers guidelines for
the design of organizational constituents based on the systems approach, enhancing
behavioral diversity on the basis of intensive self organization. Since the underlying
assumption of the paper is that the modern corporate environment is highly uncertain, the
basic managerial task is to find ways to cope with the perceived uncertainty. In order to
respond to these changes companies need to adopt new patterns of thinking and behavior,
especially managerial. The aim of this paper is to provide clear guidelines for individual
managerial behavior as their behavior is determined by their relationship with the
environment and with others in the organization thereby affecting the behavior of the entire
company .
Keywords:
business environment scanning, learning company, managerial behavior,
competitive advantages
JEL classification codes: D83, M12, M14
Introduction
Every company interacts with the environment in order o acquire, process, distribute, create
and use necessary resources in the value creation process. Resources are used to build core
competencies, which are capabilities that are valuable and unique from a customer’s point of
view, and also inimitable and non-substitutable from a competitor’s point of view (Hitt
et al.
,
2008). The most valuable and inimitable resource is a composite of tacit and explicit
knowledge developed through the process of individual, team and organizational learning.
Knowledge has already been identified as a source of innovation, customer benefits and
sustainable competitive advantages (cf. Lei
et al.
, 1996). Knowledge is firstly created in the
Corresponding author
The paper was realized in the framework of the scientific project «The development of management in the
function of the integration of Croatian economy into the EU» supported by the Ministry of Science, Education
and Sport, Republic of Croatia.
1133
individuals’ minds on the basis of information collected. Information and knowledge are
afterwards shared in the process of socialization and ultimately codified. By means of
socialization knowledge is converted from tacit to tacit, externalization renders the possibility
to transform the knowledge from tacit to explicit, combination can ensure knowledge transfer
from explicit to explicit, while internalization enables the transformation of explicit
knowledge into a new tacit form (cf. Takeuchi and Nonaka, 2004). Even though tacit
knowledge is generally considered a supreme source of competitive advantages due to its
inimitability, explicit knowledge can also hold such value when its use depends on other
inimitable organizational features such as organizational structure, culture, leadership etc. that
render possibilities for its unique combination.
The process of learning can therefore be considered a dynamic organizational capability.
According to Teece
et al.
(1997, p. 516) dynamic capabilities represent the “firm’s ability to
integrate, build, and reconfigure internal and external competences to address rapidly
changing environments”. Pettus
et al.
(2009, p. 188) also state that “capabilities involve the
organizational processes by which resources are utilized to create growth and adaptation
within changing environments”. Nobre and Walker (2011) expand the notion further and
claim that cognition, intelligence, autonomy, learning and knowledge management represent
the set of organizational capabilities. They also propose cognition as the core ability of the
organization since it is the main source of intelligence, autonomy, learning and knowledge
management in the organization. Environmental uncertainty can therefore be influenced,
governed and reduced by individual and organizational cognitive abilities. It should be
mentioned that managerial cognitive
ability is especially important because it determines the
quality of the environmental scanning process.
Environmental scanning activities act as a provider of information for the individual learning
process. Individuals learn by attributing meaning to information using existing knowledge and
mental models that determine their interpretation, which creates new forms and patterns of
knowledge and belief, ultimately influencing the way individuals and organization as a whole
respond to environmental stimuli. The process of learning is determined by managerial and
individual behavior, which can inhibit or disable learning. By actively working on improving
the environmental scanning process, managers show learning stimulating behavior, which is
then more easily translated into similar individual behavior followed by increased rate of
learning and change.
With few exceptions (such as Tan and Litschert, 1994; Elenkov, 1997) most prior research on
the relationship between environmental uncertainty and chief executive scanning behavior has
been conducted in the USA. The purpose of this research is to explore the relationship
between perceived environmental uncertainty and environmental scanning behavior further by
designing a model, which will serve as a basis for an empirical research on the sample of
Croatian companies. The model attempts to explore the connection between perceived
strategic uncertainty of the external environment and chief executive scanning activities with
the purpose to asses the extent of influence that such scanning activities have on
organizational performance within the learning company framework.
Learning companies as complex adaptive systems
Current business developments indicate that the existing management models are outdated
and that a paradigm shift is necessary. Complexity theory seems to be the most suitable in the

Želiš da pročitaš svih 11 strana?
Prijavi se i preuzmi ceo dokument.
Slični dokumenti

Ovaj materijal je namenjen za učenje i pripremu, ne za predaju.