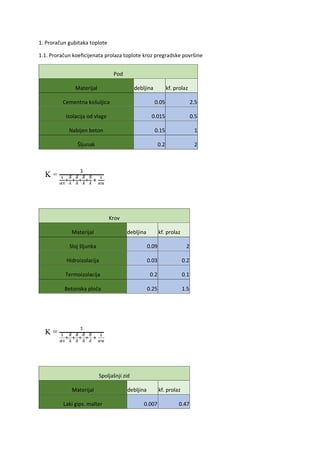
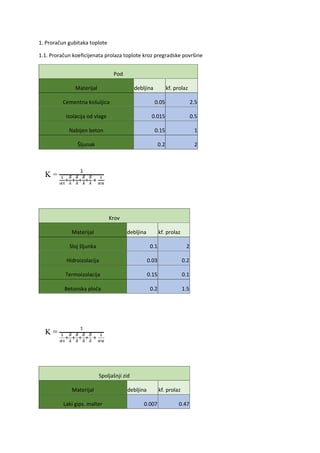
Linked Lists Pregled
FACULTY OF TECHNICAL SCIENCES – ELECTRICAL
AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING
Subject: English Language
Topic:
Linked Lists
Seminary work
Professor: Student:
Slavica Savić Lazar Nikolić 39/17
Kosovska Mitrovica, 2019.
Content:
1. Introduction…………………………………………... 1
2. Singly Linked………………………………………… 2
2.1. Insertion…………………………………………. 2
2.2. Searching………………………………………... 3
2.3. Deletion…………………………………………. 4
2.4. Traversing the list………………………………. 5
2.5. Traversing the list in reverse order……………... 6
3. Doubly Linked List………………………………….. 8
3.1. Insertion………………………………………… 9
3.2. Deletion……………………………………….... 10
3.3. Reverse Traversal………………………………. 11
Conclusion……………………………………………... 12
Resources………………………………………………. 13

2
2. Singly Linked
List Singly linked lists are one of the most primitive data structures you will find
in this book. Each node that makes up a singly linked list consists of a value, and a
reference to the next node (if any) in the list.
Figure 1.1: Singly linked list node
Figure 2.2: A singly linked list populated with integers
2.1. Insertion
In general when people talk about insertion with respect to linked lists of any
form they implicitly refer to the adding of a node to the tail of the list. When
you use an API like that of DSA and you see a general purpose method that
adds a node to the list, you can assume that you are adding the node to the tail
of the list not the head.
Adding a node to a singly linked list has only two cases:
1.
head
= 0
in which case the node we are adding is now both the
head
and
tail
of the list; or
2. we simply need to append our node onto the end of the list updating the
tail
reference appropriately.
3
As an example of the previous algorithm consider adding the following sequence
of integers to the list: 1, 45, 60, and 12, the resulting list is that of
Figure 2.2.
2.2. Searching
Searching a linked list is straightforward: we simply traverse the list checking
the value we are looking for with the value of each node in the linked list. The
algorithm listed in this section is very similar to that used for traversal in
x
2.1.4.
Želiš da pročitaš svih 15 strana?
Prijavi se i preuzmi ceo dokument.
Slični dokumenti

Ovaj materijal je namenjen za učenje i pripremu, ne za predaju.