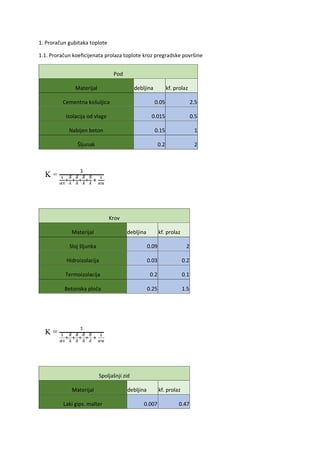
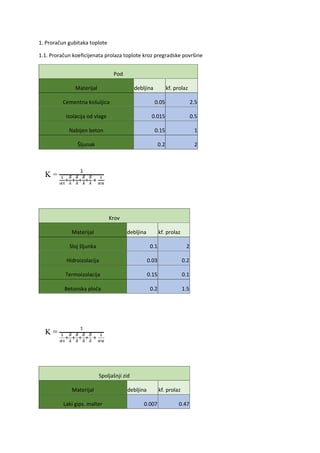
The Nervous system Pregled
The Nervous system
Nevena Mihajlović, Sandra Pejčić, Ivana Maravić | | 2019.
PAGE 1
The nervous system can be separated into divisions on
the basis of anatomy and physiology. The anatomical
divisions are the central and peripheral nervous
systems. The CNS is the brain and spinal cord. The PNS
is everything else.
Functionally, the nervous system can be
divided into those regions that are responsible for
sensation, those that are responsible for integration, and
those that are responsible for generating responses. All of
these functional areas are found in both the central and
peripheral anatomy.
Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells, neurons
and glial cells.
Neurons are the primary type of cell that
most anyone associates with the nervous system. They
are responsible for the computation and communication
that the nervous system provides. They are electrically
active and release chemical signals to target cells. Glial
cells, or glia, are known to play a supporting role for
nervous tissue.
Neurons are important, but without glial
support they would not be able to perform their function.
Synapses are the contacts between neurons, which can
either be chemical or electrical in nature.
Chemical
synapses are far more common.
Neurons are polarized cells, based on the flow of
electrical signals along their membrane. Signals are
received at the dendrites, are passed along the cell
body, and propagate along the axon towards the target,
which may be another neuron, muscle tissue, or a gland.
Many axons are insulated by a lipid-rich substance
called myelin. Specific types of glial cells provide this
insulation.
Several types of glial cells are found in the nervous system,
and they can be categorized by the anatomical division in
which they are found. In the CNS, astrocytes,

Želiš da pročitaš svih 10 strana?
Prijavi se i preuzmi ceo dokument.
Slični dokumenti

Ovaj materijal je namenjen za učenje i pripremu, ne za predaju.