Tumori jajnika u trudnoći Pregled
SVEUČILIŠTE U ZAGREBU
MEDICINSKI FAKULTET
Daria Frangen
Tumori jajnik
a u trudnoći
DIPLOMSKI RAD
Zagreb, 2017.
Ovaj dip
lomski rad izrađen je na Klinici za ginekologiju i porodništvo Kliničke bolnice
„Sveti Duh“, pod vodstvom doc. dr. sc. Berivoja Miškovića i predan je na ocjenu u
akademskoj godini 2016. / 2017.
Mentor: doc. dr.
sc. Berivoj Mišković
SADRŽAJ
ČESTALOST TUMORA JAJNIKA U TRUDNOĆI .............................................. 9
TUMORI JAJNIKA U TRUDNOĆI ...................................................................... 11
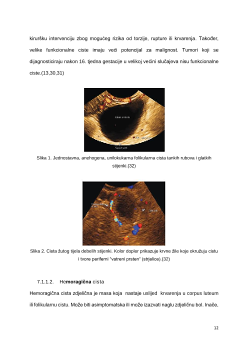
Folikularna i cista žutog tijela .......................................................... 11
gična cista .......................................................................... 12
Promjene specifične za trudnoću .......................................................... 13
Teka luteinska cista ........................................................................ 13
Luteom trudnoće ............................................................................ 14
Hiperstimulacija jajnika ................................................................... 15
Tumor lutealne hiperreakcije (hyperreactio luteinalis) .................... 16
Endometriom .................................................................................. 18
Benigni cistični teratom (dermoidna cista) ............................................ 21
Kompjuterizirana tomografija .................................................................... 35
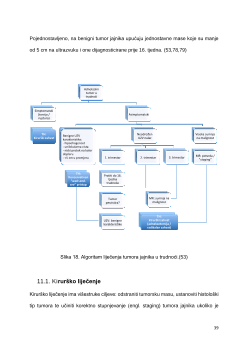
Vrijeme kirurškog zahvata ..................................................................... 40
Klasična kirurška terapija ...................................................................... 41
KOMPLIKACIJE U TRUDNOĆI ...................................................................... 46
SUMMARY
OVARIAN TUMORS IN PREGNANCY
Ovarian tumors in pregnancy are rare and their incidence ranges from 0.3 to 5.4%.
Most commonly, they are benevolent masses such as functional ovarian cysts or
benign ovarian tumors. Most benign masses in pregnancy measure less than 6 cm in
diameter and usually do not represent an obstruction in labour. The diagnosis of
ovarian tumors in pregnancy is based on physical findings, laboratory results and
imaging methods. Ultrasound is the golden standard for the diagnosis of ovarian
tumors, but it has low specificity in evaluating malignancy. Pelvic magnetic resonance
can add important information on evaluation of malignancy and tumor topography.
Treatment should be highly individualized, depending on the collected diagnostic
information, suspicion of malignancy and estimated risk of torsion, rupture or bleeding.
Torsion is the main acute complication of ovarian tumors in pregnancy and requires
urgent surgical treatment. The surgical methods used are laparotomy and laparoscopy,
and the choice of method depends on the size of the tumor, the estimation of
malignancy and the duration of pregnancy. Both surgical methods increase the risk of
obstetrical complications, such as late abortion and premature birth. If there is an
indication, it is best to surgically remove the tumor at about 18 weeks of pregnancy
because the risk of abortion at that time is relatively small. If there is a suspicion of
malignancy then surgical and other therapy may be initiated earlier.
Key words: ovary, tumor, cyst , pregnancy, diagnosis, management
Želiš da pročitaš svih 64 strana?
Prijavi se i preuzmi ceo dokument.
Slični dokumenti

Ovaj materijal je namenjen za učenje i pripremu, ne za predaju.