WAN tehnologije Pregled
WAN tehnologije
WAN mreže
• Ra
č
unarske mreže koje obuhvataju
neograni
č
en geografski prostor, sa
propusnim opsegom reda 10 kbps do 10
Gbps
WAN Technology
• A WAN is a data communications network that operates
beyond the geographic scope of a LAN.
• One primary difference between a WAN and a LAN is that a
company or organization must subscribe to an outside WAN
service provider in order to use WAN carrier network services.
• Devices on the subscriber premises are called
customer
premises equipment (CPE)
. The subscriber owns the CPE or
leases the CPE from the service provider.
• A copper or fiber cable connects the CPE to the service
provider’s nearest exchange or
central office (CO)
.
• This cabling is often called the
local loop, or "last-mile"
.
WAN Technology
WAN Service Providers
DTE and DCE
DTE and DCE
• In order for the local loop to carry data, a device such as
a modem is needed to prepare the data for transmission.
• Devices that put data on the local loop are called
data
circuit-terminating equipment
, or data communications
equipment
(DCE)
.
• The customer devices that pass the data to the DCE are
called
data terminal equipment (DTE)
.
• The DCE primarily provides an interface for the DTE into
the communication link on the WAN cloud.
• The DTE/DCE interface uses various physical layer
protocols, such as High-Speed Serial Interface (HSSI)
and V.35. These protocols establish the codes and
electrical parameters the devices use to communicate
with each other.
WAN tehnologije
• Layer 1 (RS-232, RS-449, X.21, V.35,
G.703 itd.)
• Layer 2 (HDLC, PPP, Frame Relay, X.25)
• Multilayer (ISDN, ATM, SDH/SONET)
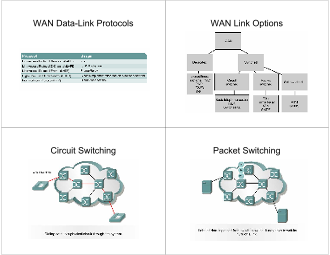
WAN Line Types and
Bandwidth
WAN Devices
CSU/DSU
•
The communications link needs signals in an appropriate format.
•
For digital lines, a
channel service unit (CSU)
and a
data service unit (DSU)
are required. The two are often combined into a single piece of equipment,
called the CSU/DSU. The CSU/DSU may also be built into the interface card in
the router.
Modem Transmission
• A modem is needed if the local loop is analog rather than
digital.
• Modems transmit data over voice-grade telephone lines
by modulating and demodulating the signal.
• The digital signals are superimposed on an analog voice
signal that is modulated for transmission.
• The modulated signal can be heard as a series of
whistles by turning on the internal modem speaker.
• At the receiving end the analog signals are returned to
their digital form, or demodulated.
Modem Transmission
Communication Server
• Communication servers concentrate dial-in
user communication and remote access to
a LAN. They may have a mixture of analog
and digital (ISDN) interfaces and support
hundreds of simultaneous users.
WAN Standards
• WANs use the OSI reference model, but focus mainly on Layer
1 and Layer 2.
• WAN standards typically describe both physical layer delivery
methods and data link layer requirements, including physical
addressing, flow control, and encapsulation.
• WAN standards are defined and managed by a number of
recognized authorities.
HDLC
• Layer 2 tehnologija koja omogu
ć
uje
prenos Layer 3 datagrama preko sinhrone
serijske linije
• Postoji HDLC ISO standard koji ne
podržava više Layer 3 protokola
• Proizvo
đ
a
č
i su razvili sopstvene
nekompatibilne HDLC derivate

Želiš da pročitaš svih 19 strana?
Prijavi se i preuzmi ceo dokument.
Slični dokumenti

Ovaj materijal je namenjen za učenje i pripremu, ne za predaju.