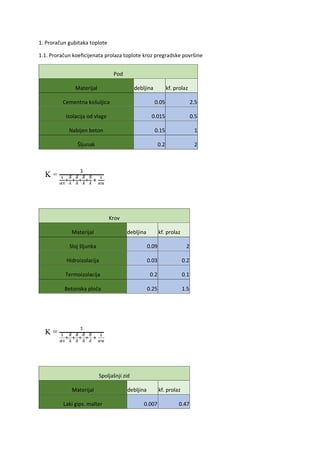
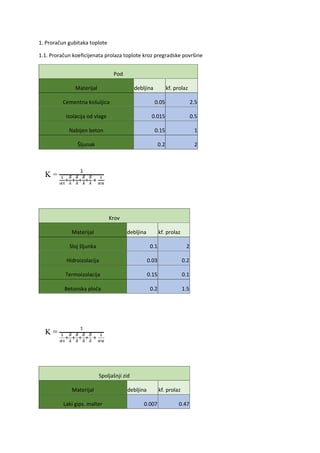
Imenice – Nouns Pregled
FAKULTET ZA POSLOVNE STUDIJE
Banja Luka
SEMINAR PAPER
THEME:
NOUNS
Menthor: Student:
prof. Tijana Lalović Mensur Husejnovic
Banja Luka, May 2013
Contents

4
that each time such a name is applied it is fixed or proper to that object. Even if there are
severalBostons or Manchesters, the name of each is an individual or proper name.
For example:
Each part of a person's name is a proper noun:
Lynne Hand,Elizabeth Helen, Ruth Jones .
The names of companies, organisations or trade marks:
Microsoft,Rolls Royce,the Round Table
Given or pet names of animals:
Lassie,Trigger,Sam
The names of cities and countries and words derived from those proper nouns:
Paris,London,New York,England,English
Geographical and Celestial Names:
the Red Sea ,Alpha Centauri, Mars
Monuments, buildings, meeting rooms:
The Taj Mahal,The Eiffel Tower, Room 222
Historical events, documents, laws, and periods:
the Civil War, the Industrial Revolution,World War I
Months, days of the week, holidays:
Monday, Christmas, December
Religions, deities, scriptures:
God ,Christ ,Jehovah ,Christianity,Judaism , Islam, the Bible, the Koran, the Torah
Awards, vehicles, vehicle models and names, brand names:
the Nobel Peace Prize, the Scout Movement, Ford Focus, the Bismarck, Kleenex ,Hoover
1.2 Common nouns
P. Gucker, Esential English Grammar, Dover Publication inc. New York, 1966. page 46.
5
A common noun is a word that names people, places, things, or ideas. They are not the names
of a single person, place or thing. Common nouns are sometimes called
class nouns
. These
nouns usually have a plural. When a common noun denotes a thing which is itself a group of
other things or persons, it is called a
collective noun
.For instance, road is a word that names
any highway outside of cities; wagon is a term that names any vehicle of a certain kind used
for hauling: the words are of the widest application. We may say, the man here, or the man in
front of you, but the word man is herehedged in by other words or word groups: the name
itself is of general application.
A common noun begins with a lowercase letter unless it is at the beginning of a sentence.
For example:
People:
man, girl, boy, mother, father, child, person, teacher, student
Animals:
cat, dog, fish, ant, snake
Things:
book, table, chair, phone
Places:
school, city, building, shop
Ideas:
love, hate, idea, pride
1.3 Collective nouns
A collective noun is a noun that can be singular in form whilst referring to a group of people
or things. Collective nouns are sometimes confused with mass nouns.
Groups of people
- army, audience, band, choir, class, committee, crew, family, gang, jury,
orchestra, police, staff, team, trio
Groups of animals
- colony, flock, herd, pack, pod, school, swarm
Groups of things
- bunch, bundle, clump, pair, set, stack.
The verb and the pronoun used with a collective noun can be in the singular or in the plural.
When a group is considered as a single unit, the collective noun is used with a singular verb
and singular pronoun.
For example:
Želiš da pročitaš svih 16 strana?
Prijavi se i preuzmi ceo dokument.
Slični dokumenti

Ovaj materijal je namenjen za učenje i pripremu, ne za predaju.