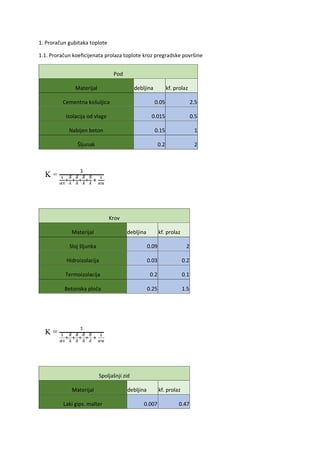
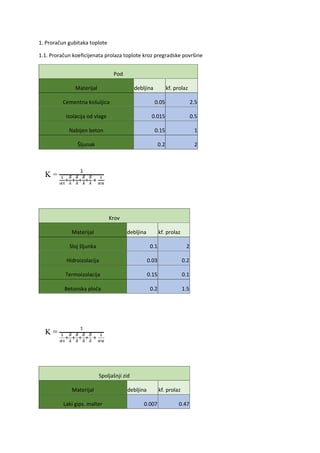
Invazivna pneumokokna bolest u dece Pregled
SVEUČILIŠTE U ZAGREBU
MEDICINSKI FAKULTET
Mario Mašić
Invazivna pneumokokna bolest u djece
DIPLOMSKI RAD
Zagreb, 2015.
SVEUČILIŠTE U ZAGREBU
MEDICINSKI FAKULTET
Mario Mašić
Invazivna pneumokokna bolest u djece
DIPLOMSKI RAD
Zagreb, 2015.

SADRŽAJ
POPIS KRATICA
SAŽETAK
SUMMARY
Sadržaj
..............................................................................1
1.2. EPIDEMIOLOGIJA INFEKCIJE UZROKOVANE S
................................2
1.3. PATOGENEZA I KLINIČKA SLIKA INFEKCIJE UZROKOVANE S. PNEUMONIAE
1.3.1. Patogeneza infekcije uzrokovane
......................................................4
1.3.2. Klinička slika infekcije uzrokovane
....................................................6
1.3.2.1. Mukozne infekcije uzrokovane
.........................................................6
1.3.2.2. Invazivna pneumokokna bolest
.................................................................................7
1.4. LIJEČENJE I PREVENCIJA INFEKCIJE UZROKOVANE
1.4.1. Liječenje infekcije uzrokovane
...........................................................9
1.4.2. Prevencija pneumokokne bolesti
................................................................................ 10
............................................................................ 14
POPIS KRATICA
ARDS
– Akutni respiratorni distres sindrom
CDC
–
Center for disease control
- Centar za kontrolu bolesti
CMV
– citomegalovirus
CSL
– cerebrospinalni likvor
HIV
–
Human immunodeficiency virus
- humani virus imunodeficijencije
ICP
–
intracranial pressure
- intrakranijalni tlak
IgA
– Imunoglobulin A
IgG
– Imunoglobulin G
IPB
– Invazivna pneumokokna bolest
KMB
– krvno moždana barijera
KOPB
– kronična opstruktivna plućna bolest
MIK
– minimalna inhibitorna koncentracija
PBP
–
penicillin binding protein
- pen
icilin vežući proteini
PCV
–
pneumococcal conjugate vacccine -
pneumokokno konjugirano cjepivo
PCR
–
polymerase chain reaction
–
lančana reakcija polimerazom
PPV
–
pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine -
pneumokokno polisaharidno cjepivo
SUMMARY
Background:
Invasive pneumococcal disease is a major health problem in children in Croatia.
Invasive diseases are bacteremia/sepsis, bacteremic pneumonia and bacterial
meningitis. Most cases of IPB's disease are caused by a limited number of
pneumococcal serotypes (less than 10). There are opportunities for prevention of IPB
in the form of conjugated vaccines.
Materials and methods:
A total of 67 pediatric patients who were treated at the Department of Pediatric
Infectious Diseases at University Hospital for Infectious Diseases "Dr. Fran
Mihaljevic "in the period of 2011 - 2013. Epidemiological characteristics of IPB and
the distribution of serotypes were analysed..
Results:
From a total of 67, 32 were male and 35 female. The mean age of the respondents is
32 months, median 23 months, and the age range from 2 months to 96 months. Of
the 67 patients, 47 had a diagnosis of bacteremia, 11 patients had been diagnosed
with a bacteremic pneumonia, and 9 patients with bacterial meningitis. Clinical
improvement following antimicrobial treatmentwas observed in 63 patients, 4 patients
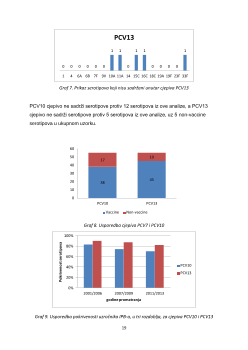
have died. 84% of invasive pneumococcal disease cases was caused by 8 serotypes
(1, 6A, 6B, 14, 18C, 19A, 19F and 23F). PCV10 vaccine could prevent 38 (70%), and
PCV13 vaccine could prevent 45 (82%) cases.
The conclusion:
Most cases of IPD in children in Croatia are caused by a limited number of serotypes
and could be prevented by vaccination using existing conjugate vaccines.
Keywords: Streptococcus pneumoniae, invasive disease, children, pneumococcal
conjugate vaccines
Želiš da pročitaš svih 36 strana?
Prijavi se i preuzmi ceo dokument.
Slični dokumenti

Ovaj materijal je namenjen za učenje i pripremu, ne za predaju.