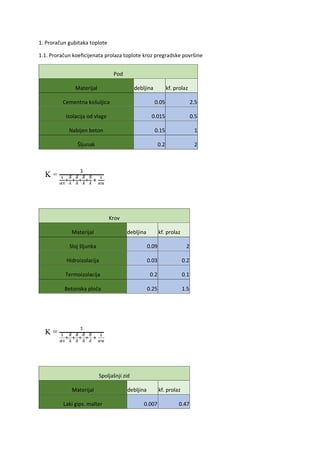
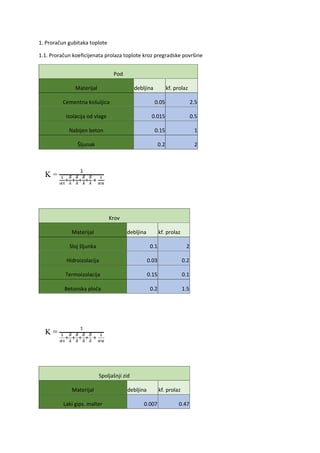
Present perfect Pregled
Contents:
1.2 Form of Present Perfect Simple
1.3 Using The Present Perfect Simple
1.4 Time Expressions with Present Perfect
................................................................................................8
2.1 Form of Present Perfect Continuous
..................................................................................................10
3. Present Perfect Simple or Present Perfect Continuous
.........................................................................13
2
Introduction
There are two tenses in English – past and present. There are
four
present tense forms: Present
simple, Present continuous, Present perfect, Present perfect continuous. In this term paper we’re going
to talk about Present Perfect Simple and Present Perfect Continuous.
The Present Perfect Tense connects the present to the past. It describes an action that happened
in the past and goes right to the present moment. The time of occurrence of the action is not mentioned.
Usually, the time is not important or is not necessary to know. It is the result of the action that matters. It
tells us the outcome to date of the action. E.g., "Frank has gone" tell us that Frank is no longer with us. The
present perfect is used to indicate a link between the present and the past. The time of the action is before
now but not specified, and we are often more interested in the result than in the action itself.
The present perfect continuous is used to refer to an unspecified time between 'before now' and
'now'. The speaker is thinking about something that started but perhaps did not finish in that period of
time. He/she is interested in the process as well as the result, and this process may still be going on, or may
have just finished.

4
1.3 Using The Present Perfect Simple
Past
Present
Future
Table 1
This table shows us that we use the Present Perfect to say that an action happened at an unspecified
time before now. We use this tense for unfinished and finished actions.
1.3.1 Unfinished Actions
I
have known
Karen since 1994.
She
has lived
in London for three years.
I
have worked
here for six months.
In these sentences we used Present Perfect tense when we want to talk about unfinished actions or
states or habits that started in the past and continue to the present. Usually we use it to say 'how
long' and we need 'since' or 'for'. We often use stative verbs.
We use 'since' with a fixed time in the past (2004, April 23rd, last year). The fixed time can be
another action, which is in the past simple (since I was at school, since I arrived)
I
have known
Sam since 1992.(
I still know her
)
I
have liked
chocolate since I was a child.
She
has been
here since 2pm. (
She is still here
)
We use 'for' with a period of time (2 hours, three years, six months).
Taken from Grammar in use –Intermediate (Raymond Murphy and William R. Smalzer -1985)
5
I
have known
Julie for ten years.(
This sentence means that action is not finished he still
knows Julie )
I
have been
hungry for hours.(
We don’t know if he is still hungry
)
1.3.2 Finished Actions
You can use the Present Perfect to describe your experience. These are actions or events that
happened sometime during a person's life. We don't say when the experience happened, and the
person needs to be alive now. We often use the words 'ever' and 'never' here.
I have been to France.
(
This sentence means that you have had the experience of being in France. Maybe you have been
there once, or several times
.)
I have been to France three times.
(
You can add the number of times at the end of the sentence
.)
I have never been to France.
(
This sentence means that you have not had the experience of going to France
)
With an unfinished time word (this month, this week, today). The period of time is still continuing.
I
haven't seen
her this month.
She
has drunk
three cups of coffee today.
I
have
already
moved
house twice this year!
We CAN'T use the present perfect with a finished time word.
NOT: I've seen him yesterday.
Želiš da pročitaš svih 17 strana?
Prijavi se i preuzmi ceo dokument.
Slični dokumenti

Ovaj materijal je namenjen za učenje i pripremu, ne za predaju.