
DDR3 RAM memorija: pregled tehnologije i primena
1
1C
DDR3 RAM Memory
Group number 1
Amina, Imran, Eldar, Zlatan
1C
2
DDR3 RAM Memory – Group number 1 – Computer Logic
Abstract
DDR3 RAM memory is interesting because it is very important topic for students and
it will follow them through life. Each new device uses DDR3 ram. RAM generally is
one very important component of a computer and it is the privilege to be on this
special time set aside. RAM is generally a very interesting topic that is important for
the process and is not boring to learn.
RAM (Random Access Memory ) is the largest part of the memory.
Good side of RAM memory is that each of its byte can be freely accessed
independently from the previous memory location, with the data we can write
(write) and load (read) from it. Each time you enter the data in a location, its
previous contents are automatically loses.
Another important characteristic of RAM is that the containing data are
reserved (kept) only during the supply voltage on it. As soon as the power
supply disappear, the entire contents of memory is lost and when the supply
voltage re-arrive (at the next turn on the computer), it is completely empty.
Because of these characteristics of RAM memory is very suitable for application
execution and data processing. Therefore, the programs and data are loaded into
RAM memory (usually the hard drive) and they use a microprocessor executing
loaded applications and their processing the obtained information. It can be done
only in this memory and therefore it is commonly called RAM memory and working
memory. Speed of the computer is directly proportional to the amount of RAM
memory. Increasing RAM memory can significantly speed up computer.
What's important for DDR3, is that it's based on SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic
Random Access Memory) design, meaning that they use a clock signal to
synchronize things. DDR3 also have higher latencies than DDR2 and of course DDR.
It is also important to know that DDR3 was raised to 8 bits. DDR2 has 4 bits and
DDR has 2. That's why DDR3 work at higher clock rates than DDR2 and DDR. We
also have a term called Resistive Termination. It's a technique to make signals
4
DDR3 RAM Memory – Group number 1 – Computer Logic
Short description of each chapter
DDR2 RAM Memory
DDR2 RAM is a double data rate synchronous dynamic random-access
memory interface. It supersedes the original DDR SDRAM specification and has itself
been superseded by DDR3 SDRAM. DDR2 is neither forward nor backward
compatible with either DDR or DDR3.
In addition to double pumping the data bus as in DDR SDRAM (transferring data on
the rising and falling edges of the bus clock signal), DDR2 allows higher bus speed
and requires lower power by running the internal clock at half the speed of the data
bus. The two factors combine to require a total of four data transfers per internal
clock cycle. With data being transferred 64 bits at a time, DDR2 SDRAM gives a
transfer rate of (memory clock rate) × 2 (for bus clock multiplier) × 2 (for dual rate) ×
64 (number of bits transferred) / 8 (number of bits/byte). Thus with a memory clock
frequency of 100 MHz, DDR2 SDRAM gives a maximum transfer rate of 3200 MB/s.
Since the DDR2 internal clock runs at half the DDR external clock rate, DDR2
memory operating at the same external data bus clock rate as DDR results in DDR2
being able to provide the same bandwidth but with higher latency. Alternatively,
DDR2 memory operating at twice the external data bus clock rate as DDR may
provide twice the bandwidth with the same latency. The best-rated DDR2 memory
modules are at least twice as fast as the best-rated DDR memory modules.
DDR3 RAM Memory
In computing, DDR3 SDRAM, an abbreviation for double data rate type three
synchronous dynamic random access memory is a modern type of dynamic random
access memory(DRAM) with a high bandwidth ("double data rate") interface, and has
been in use since 2007. It is the higher-speed successor to DDR and DDR2 and
predecessor to DDR4 synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM)
chips. DDR3 SDRAM is neither forward nor backward compatible with any earlier
type of random access memory (RAM) due to different signaling voltages, timings,
and other factors. DDR3 is a DRAM interface specification. The actual DRAM arrays
that store the data are similar to earlier types, with similar performance.
5
DDR3 RAM Memory – Group number 1 – Computer Logic
More about DDR3 RAM memory
Memory power consumption
DDR3 memory is more powerful than DDR2. DIMMs of DDR3 operate at 1.5V
compared to 1.8V for DDR2 memory. DDR3 also has further lowering power
consumption for low0voltage DIMMs that operate at 1.35V.
Power consumption by memory speed for a low-voltage 8 GB dual-rank RDIMM
DDR3 memory uses about 25% more power when running at 1333 MT/s then when
running at 800 MT/s. DDR3 memory uses about 30 % less power than DDR2
memory when running at the same speed (800 MT/s). At 133 MT/s, DDR3 uses
about the same power as DDR2 memory while providing an improvement in
maximum bandwidth.
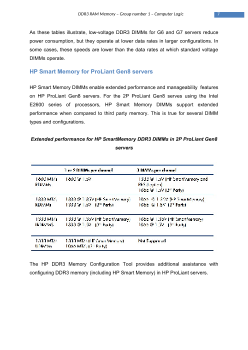
The new 1600 MT/s DDR3 RDIMMs for the ProLiant Gen8 serves use 1.5V and
consume the most power. Running at 1600 MT/s, DDR3-1600 memory uses about
15% more power that the equivalentDDR-1333 memory in G6 and G7 servers.
DDR3 has two power savings modes that the memory controller can employ to
reduce memory power consumption-CKE power and self-refresh mode. With CKE

Ovaj materijal je namenjen za učenje i pripremu, ne za predaju.
Slični dokumenti



























































